How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and this guide provides a comprehensive answer. From understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics to mastering pre-flight checks and navigating complex flight maneuvers, we’ll cover everything you need to know to safely and effectively pilot your own drone. We’ll explore essential safety procedures, legal considerations, and even delve into advanced features and applications.
This guide aims to empower you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will dissect the intricacies of drone controls, explaining the functions of the throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll, and guiding you through various flight modes. We’ll also detail the crucial steps involved in flight planning and mission execution, ensuring you can confidently navigate your drone through various environments. Furthermore, post-flight procedures, maintenance, and legal compliance will be thoroughly addressed, leaving no stone unturned in your journey to becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Drone Types and Their Operation

Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones, outlining their operational differences, pre-flight checks, and control interfaces.
Multirotor, Fixed-Wing, and Single-Rotor Drone Operation
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters or hexacopters, utilize multiple rotors for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and omnidirectional movement. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, require a runway for takeoff and landing, offering longer flight times and greater range but limited maneuverability. Single-rotor drones, or helicopters, provide VTOL capabilities with more precise control and stability compared to multirotors, but are generally more complex to operate.
Pre-Flight Checks for Different Drone Types
- Multirotor: Check rotor blades for damage, ensure battery is fully charged and securely connected, inspect the gimbal (if present), and calibrate the compass.
- Fixed-wing: Verify the proper installation of the wings and tail, check the control surfaces for damage, ensure the battery is securely mounted and charged, and inspect the propeller for damage.
- Single-rotor: Inspect the main rotor blades for damage, verify the tail rotor’s functionality, ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected, and check the swashplate mechanism.
Comparative Analysis of Drone Control Interfaces
| Drone Model | Controller Type | Control Features | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | Dedicated Handheld Controller | Gimbal control, intelligent flight modes, obstacle avoidance | Easy |
| Autel Evo II | Dedicated Handheld Controller | Multiple flight modes, obstacle sensing, high-resolution image transmission | Easy to Moderate |
| Parrot Anafi | Smartphone App | Basic flight controls, limited intelligent flight modes | Easy |
| Eachine E58 | Dedicated Handheld Controller | Basic flight controls, headless mode | Easy |
Pre-Flight Procedures and Safety
Prioritizing safety is paramount in drone operation. This section will detail the essential steps for a safe drone launch, including location selection, weather checks, and pre-flight inspections. Emergency procedures will also be discussed.
Safe Drone Launch and Location Selection
Select a location free from obstacles and away from populated areas. Check the weather conditions – avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow. Ensure you have a clear line of sight to the drone at all times. Always obtain necessary permissions before flying in restricted airspace.
Pre-Flight Safety Checklist
- Battery charge level
- Propeller condition
- Gimbal functionality (if applicable)
- GPS signal strength
- Controller battery level
- Radio signal strength
Emergency Procedures
In case of unexpected events such as loss of signal, battery failure, or mechanical malfunction, immediately initiate an emergency landing procedure. Most drones have a “return to home” (RTH) function that can be activated. If RTH fails, attempt to manually control the drone to a safe landing zone. If the drone is uncontrollable, prioritize safety and minimize potential damage or injury.
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective flight. This section will explain the functions of a typical drone controller, different flight modes, and illustrate a typical flight maneuver.
Drone Controller Functions
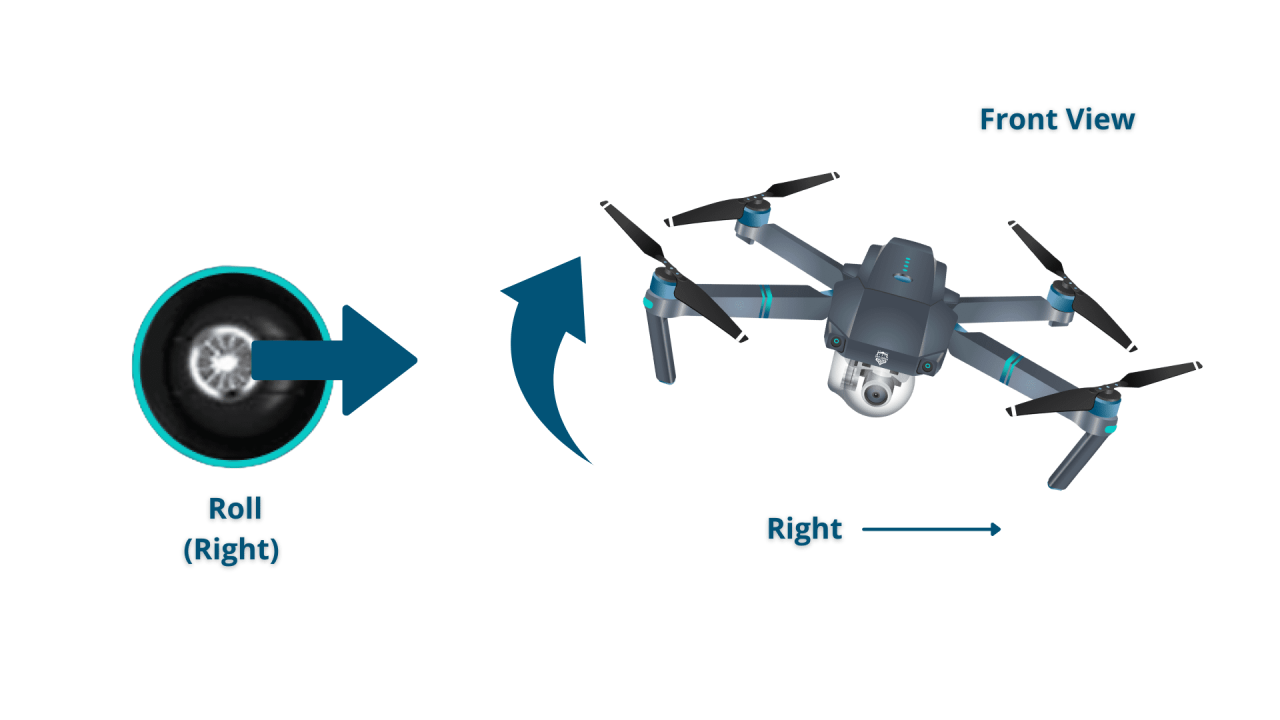
A typical drone controller features sticks for controlling throttle (vertical movement), yaw (rotation around the vertical axis), pitch (forward/backward tilt), and roll (side-to-side tilt). Buttons control various functions like camera settings, flight modes, and return-to-home.
Flight Modes
GPS mode utilizes GPS signals for precise positioning and stability, ideal for long-range flights. Attitude mode relies on the drone’s internal sensors, allowing for more agile maneuvers but requiring more pilot skill. Other modes, such as Sport mode and Cinematic mode, offer varying degrees of control and responsiveness.
Visual Representation of a Drone Flight Path

Imagine a drone starting at point A. It ascends vertically to point B. Then, it moves horizontally to point C, making a gentle right turn. It descends slightly to point D before making a sharp left turn to point E, maintaining a relatively constant altitude. Finally, it moves directly back to point A, completing the maneuver.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Effective flight planning is crucial for successful drone missions. This section will Artikel a step-by-step guide for planning a drone flight, including waypoint and altitude settings, and discuss maneuvering in complex environments.
Step-by-Step Guide for Drone Flight Mission Planning
- Define the mission objective.
- Select a suitable flight location and obtain necessary permissions.
- Plan the flight path, including waypoints and altitude settings.
- Conduct pre-flight checks.
- Execute the flight plan, monitoring the drone’s status.
- Perform post-flight checks and data analysis.
Examples of Flight Maneuvers
Orbiting a point of interest involves setting a circular flight path around a specific location, useful for capturing panoramic views. Following a pre-programmed route involves defining a sequence of waypoints for the drone to follow autonomously, ideal for aerial surveys or inspections.
Challenges and Solutions for Flying in Complex Environments, How to operate a drone
Flying near obstacles requires careful planning and precise control. Using obstacle avoidance features (if available) and maintaining a safe distance from obstacles are crucial. Windy conditions can affect stability; adjust flight parameters accordingly or postpone the flight until conditions improve.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are essential for prolonging the lifespan and functionality of your drone. This section will Artikel essential steps for securing the drone, a maintenance schedule, and storage/transport methods.
Securing the Drone After Flight
After landing, power off the drone and securely store the battery in a designated case. Inspect the drone for any damage and clean any debris from the propellers and body. Store the drone in a cool, dry place to prevent damage.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
- Daily: Inspect propellers, body, and landing gear for damage.
- Weekly: Clean the drone body and propellers.
- Monthly: Check battery health, calibrate sensors, and inspect motor mounts.
Drone Storage and Transportation
Use a hard-shell case to protect the drone during transport. Store the drone in a cool, dry, and dust-free environment. Avoid exposing the drone to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires adherence to local and national regulations. This section will cover essential regulations, permits, and legal implications of violations.
Essential Drone Regulations
Regulations vary by location but generally cover areas like airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and regulations before operating a drone.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. This is especially true for commercial drone operations or flights in restricted airspace. Failing to obtain necessary permissions can lead to legal consequences.
Legal Implications of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, legal action, and even criminal charges. Responsible drone operation includes understanding and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations.
Advanced Drone Features and Applications
Modern drones offer a range of advanced features and are utilized across various sectors. This section explores advanced features, diverse applications, and compares drone capabilities for specific uses.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your piloting skills. Ultimately, responsible and skillful drone operation ensures both safety and successful missions.
Advanced Drone Features
Obstacle avoidance systems utilize sensors to detect and avoid obstacles during flight. Follow-me mode allows the drone to automatically track a subject, while waypoint navigation enables pre-programmed flight paths.
Drone Applications
Drones are used extensively in photography and videography for capturing stunning aerial footage. They are also employed in inspections, delivering goods, surveying land, search and rescue operations, and precision agriculture.
Drone Capabilities for Specific Applications
| Application | Drone Model | Key Features | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerial Photography | DJI Mavic 3 | High-resolution camera, gimbal stabilization | High-quality images, easy to use; Can be expensive |
| Infrastructure Inspection | Autel EVO II | Thermal imaging, zoom capabilities | Detailed inspections, efficient; Requires specialized training |
| Delivery Services | Amazon Prime Air (hypothetical example) | Autonomous flight, package delivery system | Fast delivery, reduced costs; Requires robust infrastructure and regulatory approval |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the complexities of drone piloting, from pre-flight preparation to post-flight maintenance. By diligently following the safety guidelines and adhering to legal regulations, you can confidently and responsibly explore the exciting world of drone technology. Remember that continued practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and skilled drone pilot.
Clarifying Questions
What is the maximum flight time for a typical drone battery?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model and battery size, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to check out for comprehensive guidance is this helpful guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice and experience will further refine your skills, ensuring safe and effective drone operation.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to switch to a failsafe mode (if available) and try to land the drone in a safe area. If recovery isn’t possible, report the incident to the relevant authorities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is recommended before each flight, especially if the drone has been moved significantly or experienced a strong magnetic field interference.